Etsuko Uno
The Origin of Breast Cancer | Drew Berry, Etsuko Uno
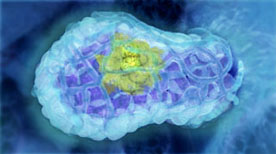
This animation visualises research published in Nature Medicine (Vol 15, Issue 8, 2009) by the laboratory of Jane Visvader and Geoffrey Lindeman. The mammary gland is comprised of three main cell types; alveolar, ductal and myoepithelial cells. Breast stem cells can develop into any of the three cell types through a series of intermediate cell stages. One intermediate is the luminal progenitor cell, which develops into either alveolar or ductal cells. The paper describes how an aberrant form of a luminal progenitor cell is involved in the development of some forms of breast cancer.
» View the animationThe Control of Breast Stem Cells | Drew Berry, Etsuko Uno
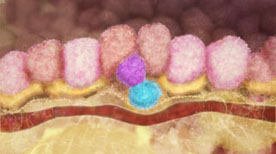
This animation illustrates how breast stem cells respond to steroid hormone despite the cells not having any steroid receptors. The animation illustrates the research published in Nature (Vol 465, Issue 7299, 2010) by the laboratory of Jane Visvader and Geoffrey Lindeman.
» View the animationBreast Stem Cells | Drew Berry, Etsuko Uno

An overview of the human mammary gland with a focus on the role of breast stem cells during pregnancy. The primary function of the mammary gland is to produce milk to nourish young offspring. The mammary gland is comprised of three main cell types; alveolar, ductal and myoepithelial cells. During pregnancy, the mammary gland increases in size due to the action of breast stem cells, which can mature into any of the three mammary gland cell types.
» View the animationDiabetes (type I) | Etsuko Uno
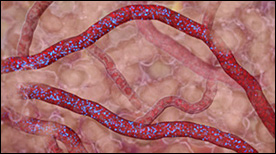
This animation explores insulin production both in the normal case as well as in the development of Type 1 Diabetes, when insulin production is disrupted.
» View the animationClonal Selection Theory | Etsuko Uno
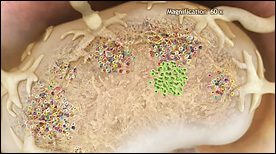
‘Fighting Infection by Clonal Selection’ was created to commemorate the 50th anniversary of a revolutionary theory called ‘Clonal Selection’ by Nobel Laureate, Sir Frank Macfarlane Burnet. The animation shows how clonal selection works during a bacterial infection of the throat.
» View the animation




